Ultra-high Sensitive Measurements
- A cross-flow modulation dual-beam non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) analyzer provides continuous and stable zero drift-free measurements.
- Minimum detection limit (MDL) of 10ppb which can support applications where high accuracy measurements are required.
Measurement of trace impurities in a balance gas
- Representative gases such as N2, O2, He, Ar, H2 and Air are supported.
Easy maintenance-free operation
- Operator friendly screen menus simplify analyzer operation, calibration and measurements
- No optical alignment ever required.
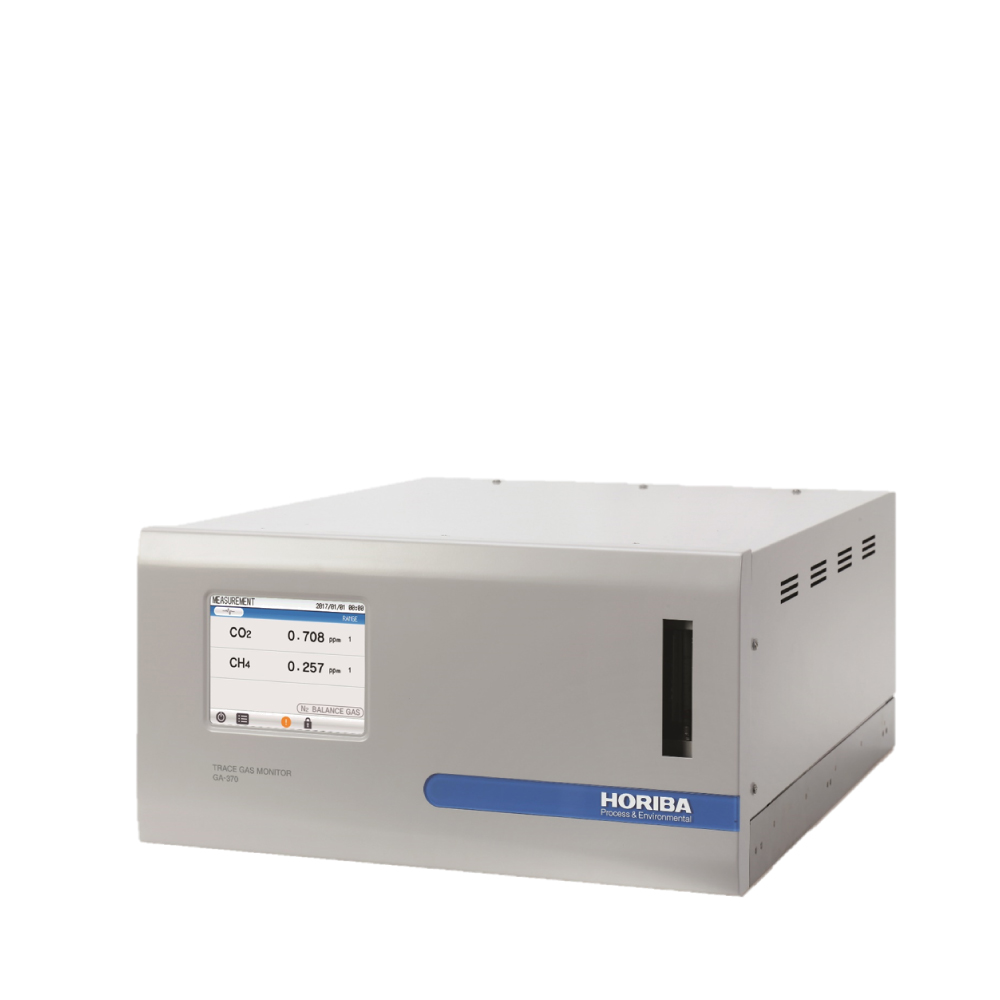
- A touch color LCD display allows operators to view graphs of accumulated data.
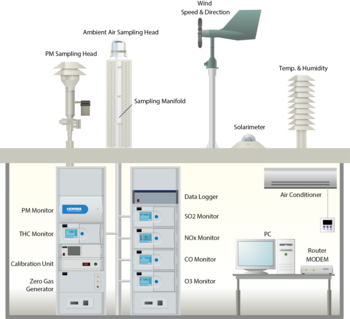
Application
- Trace Impurities Monitoring at Air Separation Plants
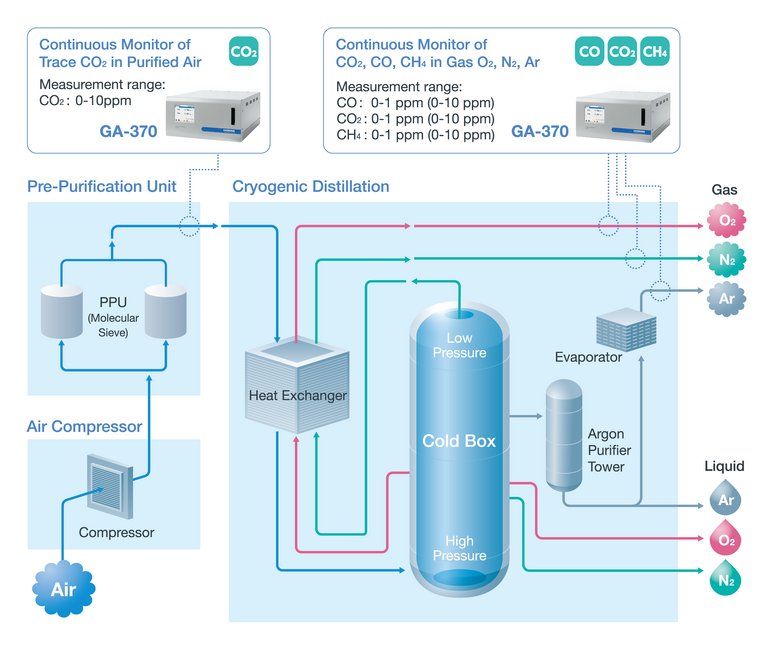
Air separation plant separates atmospheric air into its primary components oxygen (O2), nitrogen (N2), and argon (Ar) by distillation at cryogenic temperatures.
Separation of air is performed using the difference in the boiling points of each constituent gas in the distillation unit, but the air must be treated in the pre-purification unit (PPU) before getting into cryogenic distillation process. PPU is designed to remove water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2), and other impurities contained in the air to ensure water and CO2 does not enter into the distillation unit, where it could cause plugging in the process and create the risk of explosion.
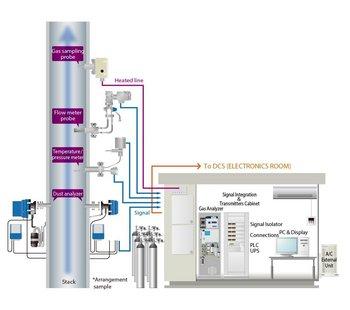
The HORIBA GA-370 Trace Gas Monitor is a useful tool for continuous monitoring of impurities that might be present in the separated gas for safety control. Also, it could be used for measurement of impurities (CO, CO2, CH4) in final product of O2, N2 and Ar for quality assurance.
Principle of Measurement
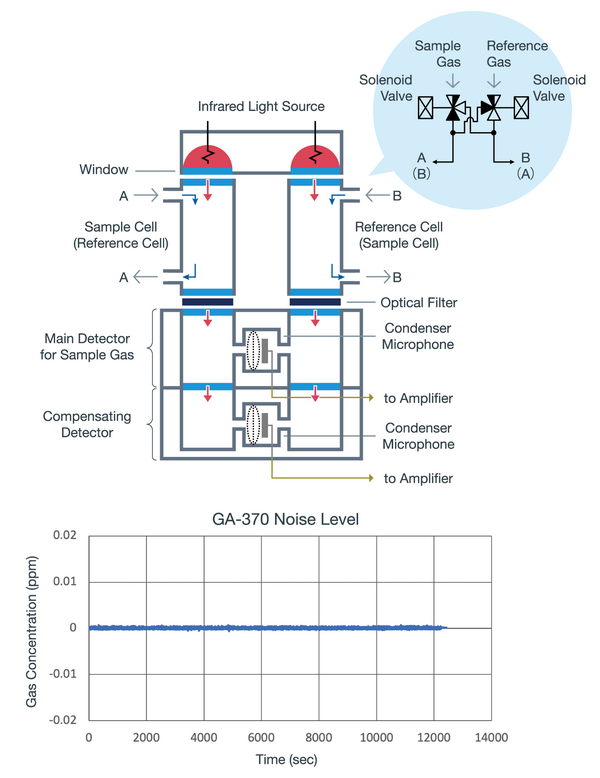
- Cross-Modulation Dual-Beam Non-Dispersive Infrared Method
Cross-Modulation NDIR method uses a solenoid valve that switches at a fixed cycle (e.g., 1 Hz) to synchronously and alternately flow a sample gas and a reference gas into the one gas cell to obtain a modulated concentration signal of the gas to be measured.
In this method, when the sample gas and the reference gas are the same gases (zero point), no modulation signal is generated. Absence of mechanical parts such as a rotating sector enables long-term stable output signal.
In cross-modulation dual-beam NDIR method, the use of double beam (light source) and a double cell allows the sample gas and the reference gas to flow alternately into the two cells, the diaphragm of the condenser microphone inside the detector moves to the left and to the right, providing twice the amount of signal comparing with the method when using a rotating sector, thereby improving the SN ratio.
The graph shows the noise level of the cross-modulation dual-beam non-dispersive infrared method, which is extremely low and stable. Thus, even in the measurement of trace concentrations of impurities in high-purity gases, this zero-drift free method provides long-term stability and low noise level.
Related Applications
Explore more
▶ Hydrogen Quality Check for FCV at On-Site Hydrogen Station