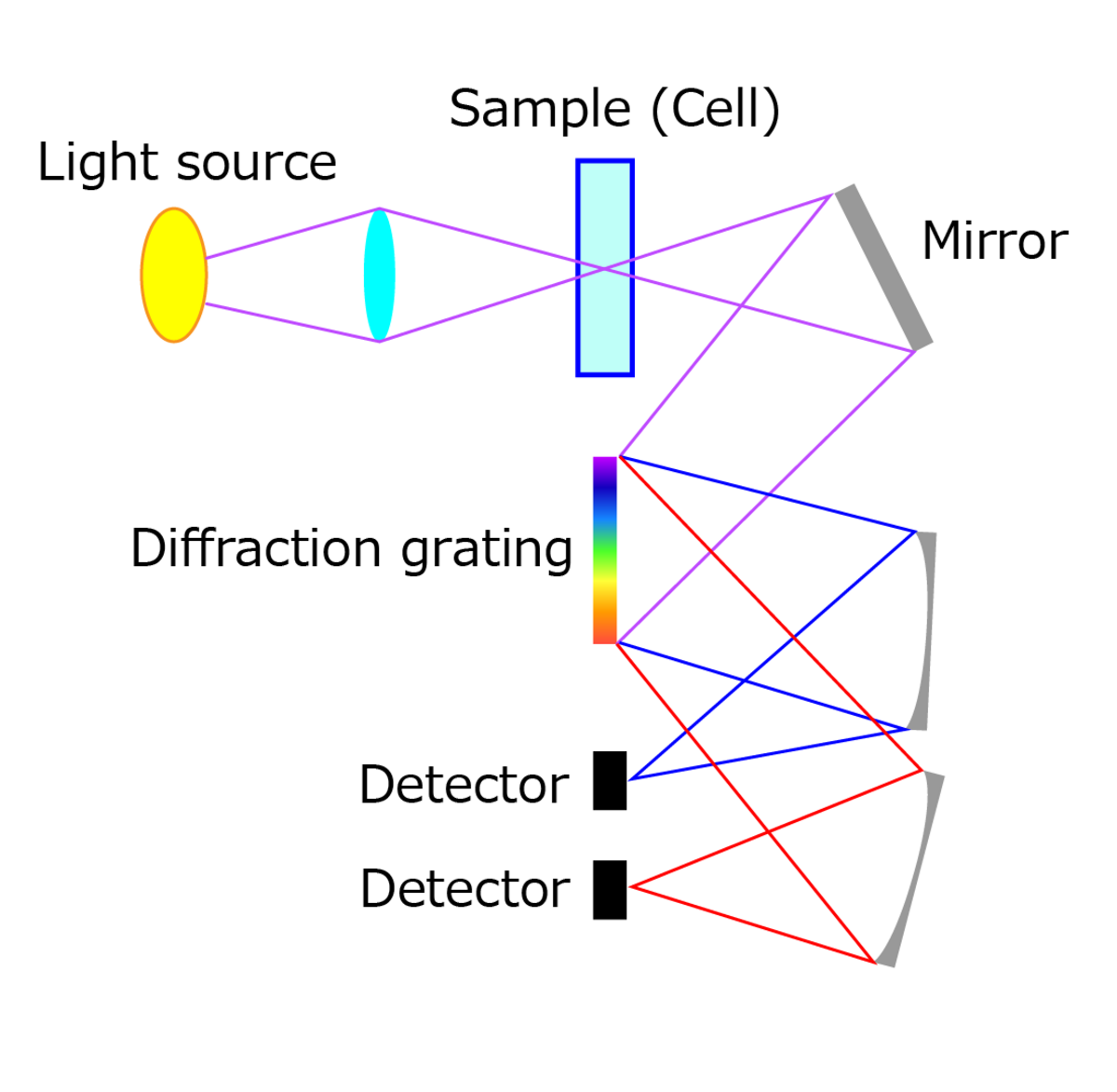
Absorption spectroscopy is a method of detecting concentration by measuring how much light is absorbed as it passes through a sample.
First, light from a light source is shone onto a cell with the sample to be measured. A mirror reflects light passing through the sample and transmits it to an optical component called a diffraction grating. The diffraction grating has the ability to separate the light beam into ultraviolet, near-infrared, and other individual wavelengths, before reflecting them at different angles. Each decomposed wavelength is directed to its own detector, which quantifies how much of that wavelength was absorbed by the sample.
To determine a sample’s concentration, samples with known concentrations are prepared and measured beforehand. Different types of these samples are measured to collect data on how much light of each wavelength is absorbed at each concentration. The collected data is then analyzed to create a calibration curve that represents the relationship between the sample’s concentration and light absorption.
This calibration curve is used to convert the amount of light absorbed to concentration, enabling detection of the sample’s concentration.
Chemical Solution Monitoring System
非接觸式化學濃度監測儀
光纖式熱磷酸濃度監測儀
光纖式化學濃度監測儀
光纖式化學溶液濃度監測儀
高精度、高穩定性化學濃度監測儀
獨立式化學濃度監測儀