

Vitamins are organic compounds required as a vital nutrient for a living organism that is not synthesized in sufficient quantity by the organism, so they must be obtained from the diet. Vitamins are classified by their biological and chemical activity, not by their structure. They are grouped under an alphabetized generic descriptor title such as vitamin A that includes the compounds retinal, retinol, and four carotenoids.
Several vitamin compounds were purchased commercially and prepared following published procedures. The particle size was then performed using the SZ-100 Nanoparticle Size Analyzer.
Also known as thiamine, vitamin B1 is water miscible with chemical formula C12H17N4OS. The thiamine was prepared at 300 mg/mL using filtered DI water. This was then passed through a 20 nm filter using a syringe into a cleaned glass cell. The sample was analyzed and the final result was reported on a volume basis. The mean diameter by volume basis was reported at 0.4 nm.
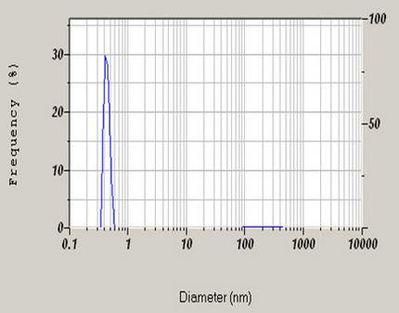
Particle size distribution for a Vitamin B1 dispersion.
Also known as ascorbic acid, Vitamin C is water soluble, so this sample was diluted in toluene and measured in the standard glass cell ay 90°. The arithmetic mean was reported at 59.8 nm.
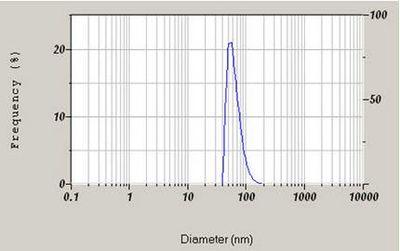
Particle size distribution for a Vitamin C dispersion.
Vitamin E refers to a group of eight fat soluble compounds that include both tocopherols and tocotrienols. The sample used in this analysis was vitamin E ester acetate. The sample was prepared in filtered DI water and measured at the 90° sizing detector using a standard disposable plastic cell. The reported arithmetic mean on a volume basis was 44.6 nm.
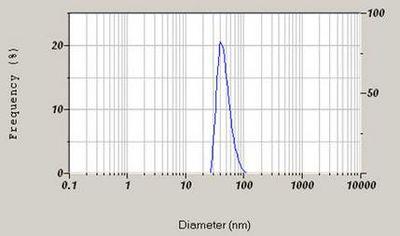
Particle size distribution of Vitamin E dispersion.
Laser Scattering Particle Size Distribution Analyzer
Nanoparticle Analyzer
Do you have any questions or requests? Use this form to contact our specialists.