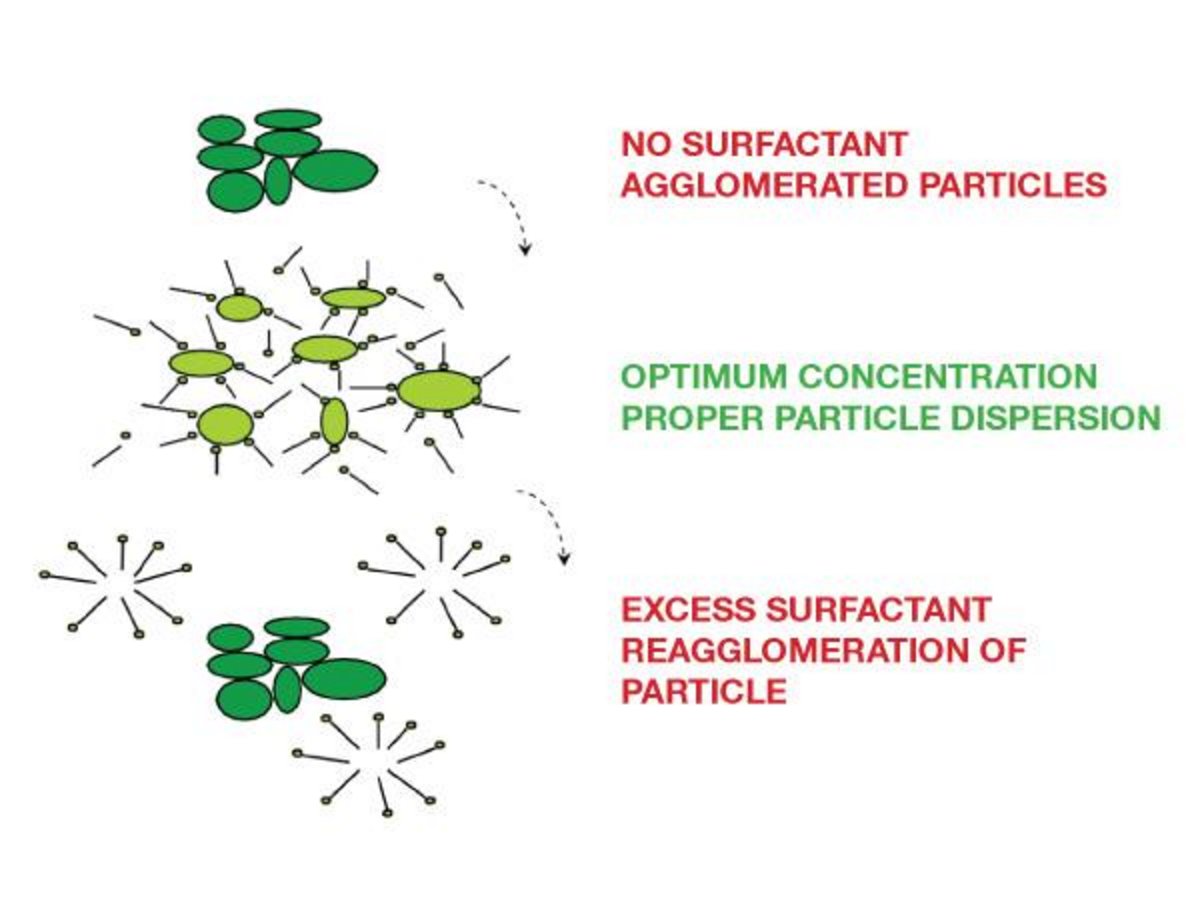
The term surfactant is derived from SURFace ACTive AgeNTS. Surfactants are molecules that decrease surface tension and interfacial tension between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants distribute themselves to have a higher concentration at the solid/liquid interface, than in the surrounding liquid phase. This excess concentration arises at the solid/liquid interface because the surfactant's molecular structure consists of one portion that is soluble in a liquid, and another portion which is insoluble in the same liquid.
Whereas many solutes have some slight increase in concentration near an interface, surfactants have a strong tendency to concentrate near the surface. The surfactant molecules preferentially orient themselves with the liquid-insoluble portion adsorbed on the surface of the solid particle, and the liquid-soluble portion sticking out into the liquid phase. This causes individual particles to become better dispersed in the liquid.
Laser Scattering Particle Size Distribution Analyzer
Laser Scattering Particle Size Distribution Analyzer
Do you have any questions or requests? Use this form to contact our specialists.