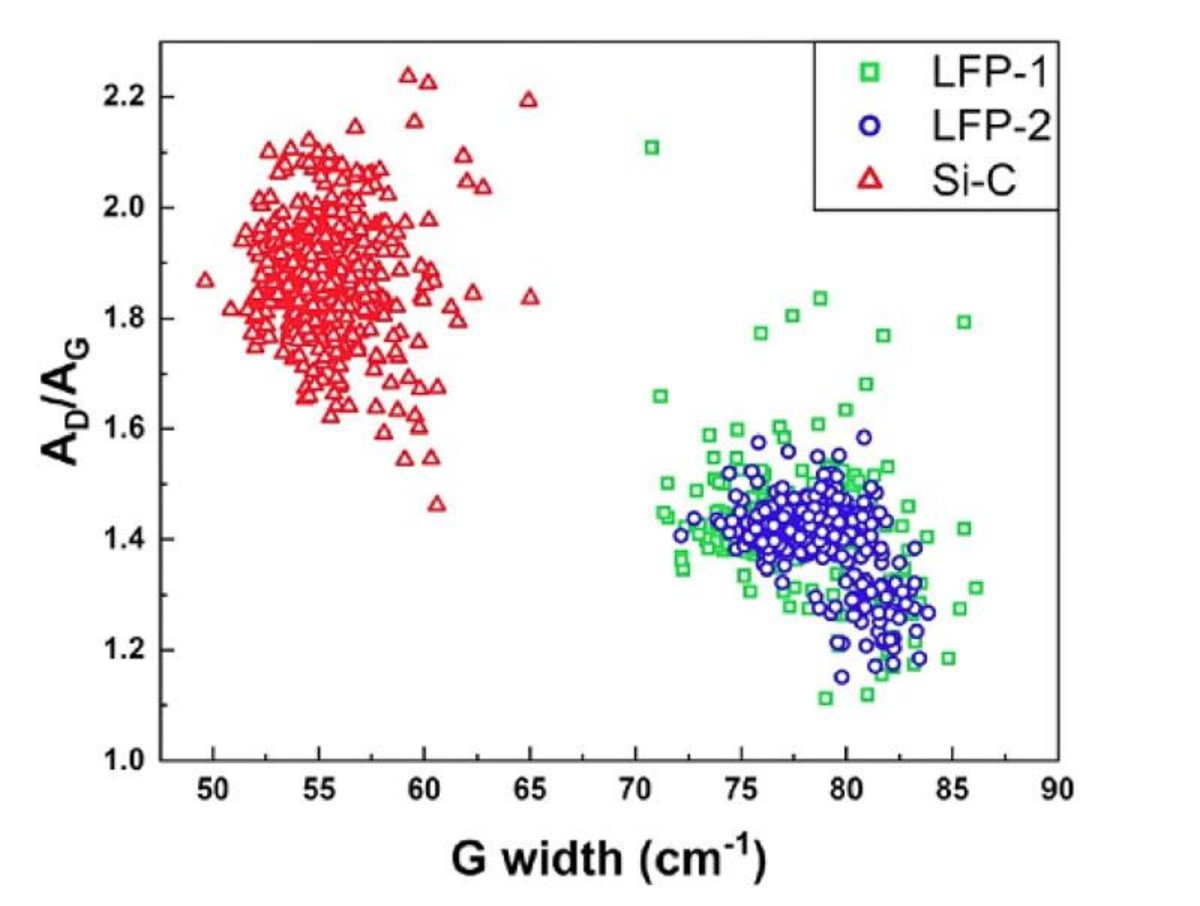
As the requirements for electric vehicles and other portable devices become more and more demanding, the need for higher performance batteries and the ability to monitor the battery material’s physical and chemical characteristics will continue to increase. Of the novel battery materials finding more usage in rechargeable lithium-ion batteries are lithium iron phosphates (LFPs), used to comprise the cathode, and carbon-coated silicon (Si@C), used to make the anode. LFP is of interest because of higher safety, lower cost, and longer cycle life compared to nickel cobalt-based batteries, but on their own have poor electrical conductivity, so it is coated with carbon to improve its conductivity. Carbon-coated silicon is of interest as a potential anode material as silicon has ten times the theoretical capacity of the typical graphite anode, while the carbon coating helps to provide structural stability and improves its conductivity.
Particle size is an important parameter to monitor as it affects nearly all performance parameters for battery materials, but in general smaller and narrow distributions are better than wider and coarser distributions. Smaller particle sizes in general lead to increased surface area availability for electrochemical reactions, but nanosized material can lead to poor packing density and lower volumetric energy density.
激光粒度分析仪
高性能全自动拉曼光谱
如您有任何疑问,请在此留下详细需求信息,我们将竭诚为您服务。