HORIBA offers a wide range of gas analysis solutions for hydrogen (H2) and ammonia (NH3) combustion research and development, meeting customers' measurement needs. We also provide our measurement solutions not only for H2 and NH3, but also for NOx, N2O, O2, and CO, as well as the turnkey solutions for test facility construction, including the conversion of existing engine benches to hydrogen engine benches.
In the automotive and marine fields, "hydrogen engines," which run engines (internal combustion engines) with the power of hydrogen combustion, are again attracting attention especially in Japan and Europe.
Also, in the power generation field, R&D and demonstration of mixed combustion power generation (hydrogen is mixed with conventional fossil fuels) and exclusive combustion power generation (hydrogen alone is used to generate power) are being conducted. Ammonia, which contains no carbon like hydrogen, has an energy density 1.7 times that of liquid hydrogen, making it highly efficient for storage and transportation.
Table of Contents
To achieve carbon neutrality, engines and power generation using "exclusive combustion," (both hydrogen and ammonia are combusted at 100%) is necessary to avoid CO2 emissions. On the other hand, CO2 emissions reduction by modifying existing equipment, facilities and infrastructure, and by mixed combustion (fossil fuels are mixed with conventional fuels for combustion) is also expected as a transition step toward carbon neutrality.
As technical issues, hydrogen combustion requires countermeasures against abnormal combustion and NOx generation due to faster combustion speed, lower calorific value, and higher adiabatic flame temperature than conventional fuels, as well as improvement of combustion efficiency. In addition, ammonia combustion requires countermeasures against unstable combustion and the generation of NOx and N2O (which has a global warming potential approximately 298 times that of CO2) due to its slow combustion speed, low calorific value, and nitrogen content compared to conventional fuels, as well as improvement of combustion efficiency.
* Our drawing based on NEDO "Fuel Ammonia Supply Chain Establishment"
CRMT is an engineering private company working on the development of alternative energy engines and vehicles, and plans to pioneer the first "Center of Expertise in Hydrogen" in France in partnership with HORIBA, enabling customers to access state-of-the-art hydrogen solutions at every step of the process, meeting all their needs and challenges across the full hydrogen value chain, from generation to storage and utilization.
Through this partnership, Pipo Moteurs, a small and medium-sized company in the Ardèche area of France, has partnered with CRMT and HORIBA France, a French subsidiary of HORIBA, to evaluate a newly developed hydrogen fuel engine. The engine will be installed in a vehicle that will compete in the 2023 Dakar Rally to evaluate its behavior under severe driving conditions.
For more information on our partnership with CRMT, please see this press release.
Hydrogen engines are expected to become a new power source for automobiles. The components and development environment of gasoline and diesel engines, as well as the high level of expertise in internal combustion engines, can be diverted and utilized, and hydrogen engines have the potential to be less expensive than FCVs. Furthermore, hydrogen as fuel does not require the same level of purity as fuel cells, and is therefore being considered as a means of utilizing hydrogen. On the other hand, various issues must be solved, such as abnormal combustion and cooling loss due to excessive premature ignition and reduction of NOx emissions during heavy-load operation.
The shipping industry has been working internationally to reduce CO2 and other greenhouse gases (GHG). International shipping is counted in the International Maritime Organization (IMO), while domestic shipping is counted in national emissions, and each country is considering its own response under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). The IMO's long-term goal is to achieve zero GHG emissions from international shipping as early as possible in the 21st century, and against this backdrop, the shipping industry is also focusing on the use of hydrogen and ammonia-fueled engines.
Reference link: Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, "Jisedai sempaku no kaihatsu project no kenkyukaihatsu/ shakaijissou keikaku (an) ni tsuite" [Draft R&D and Social Implementation Plan for the "Development of Next-Generation Ships" Project]
HORIBA has developed various applications with many customers in the measurement and evaluation of engine performance and exhaust gas in internal combustion engines for automobiles and ships, gas and water quality measurement in power generation facilities, and material analysis at the nano level. Combining our accumulated measurement know-how, we provide total performance evaluation solutions for the development and demonstration of engines that use hydrogen and ammonia as fuel and gas turbines for power generation.
HORIBA Solutions >>
For measuring fuel mass flow: Fuel Flow Meter (contact us)
For testing engine performance: Engine Dynamometer
For Measuring multi-component gas : FTIR Exhaust Gas Analyzer FTX-ONE
For measurement of nitrogen gas such as N2O and NH3: Motor Exhaust Gas Analyzer MEXA-ONE
For measuring exhaust gas flow rate from engines directly: Ultrasonic Exhaust Flow Meter EXFM-ONE
For measuring the number of solid particles in exhaust: Solid Particle Counting System MEXA-2000SPCS Series
For measuring hydrogen gas concentration: Hydrogen Gas Analyzer HyEVO
Test Integration Platform: Test Automation System STARS Series
In the field of power generation, the development of large-scale power generation system using hydrogen and ammonia as fuels, which does not emit CO2 during combustion, is progressing. In the future it is expected that power generation will be shifted to gas turbines of dedicated combustion, and in the meantime the mixed combustion power generation will be put to practical use to reduce CO2 emissions step by step.
Currently, the demonstration and evaluation of small-scale dedicated hydrogen power generation has been completed, and a combustor for large-scale mixed combustion power generation is in the development and demonstration stage. In the area of ammonia power generation, a demonstration of mixed combustion power generation using existing coal-fired facilities is being conducted, and in the area of Gas Turbine Combined Cycle (GTCC) power generation, a technology is being developed to generate electricity by combustion of H2 obtained through the pyrolysis of ammonia, with mixing natural gas.
The technical challenges for hydrogen power generation are the prevention of backfires*, combustion vibrations in combustors and the reduction of air pollutant NOx emissions. In ammonia power generation, the major challenge is to reduce NOx (especially NO due to excess oxygen supply) and N2O emissions.
*Backfire: A phenomenon in which the flame in the combustor travels backwards through the fuel being fed.
HORIBA has been providing various solutions for continuous gas measurement required for development of new technologies for power generation facilities, reduction of air and water pollutant emissions, and improvement of facility operating rates. In the combustion evaluation of hydrogen and ammonia, we provide customers with optimal solutions by combining gas analyzers and sampling, utilizing our accumulated know-how for research and development requiring high-precision measurement and for demonstration evaluation requiring long-term stable operation at sites with severe environmental conditions.
●Power Generation by Hydrogen Mixed and Exclusive Combustion
Combustors are being developed to improve combustion efficiency while preventing backfires and combustion oscillations, with reducing the air pollutant NOx. In the development of gas turbines for hydrogen power generation, it is necessary to evaluate the hydrogen as fuel and unburned hydrogen and NOx by continuous gas measurement.
●Power Generation by Ammonia Mixed and Exclusive Combustion
While developing and demonstrating ways to improve the ammonia mixed combustion rate in coal-fired power generation facilities and Gas Turbine Combined Cycle (GTCC) power generation facilities, we are also developing technologies to connect to exclusive combustion power generation. Development of an ammonia decomposer that combines ammonia with a catalyst and thermally decomposes it to produce hydrogen is also underway, as is the development of power generation by applying an ammonia decomposer and a combustor for hydrogen combustion.
●Demonstration of Ammonia Mixed Combustion in Existing Thermal Power Plants and Development of Turbines for Ammonia Power Generation
In addition to conventional gas measurement of air pollutants including NOx, measurement of unburned NH3 and N2O is especially necessary. In addition, for performance evaluation of gas turbines in demonstration facilities, it is important that gas analyzers and sampling equipment operate stably over the long term without failure or performance degradation under severe field conditions.
HORIBA Solutions >>
For measuring hydrogen gas concentration: Hydrogen Gas Analyzer HyEVO
For measuring hydrogen in high concentration/hazardous area: Explosion-proof Thermal Conductivity Analyzer TCA-51d/p
For measuring combustion gas/exhaust gas (for R&D): Multi-component Gas Analyzer VA-5000 Series
For monitoring air pollutants: Stack Gas Analysis System ENDA-5000 Series
For Measuring NOx by portable analyzers: Portable Gas Analyzer PG-300 Series
When hydrogen and ammonia are used as fuels in engines and gas turbines for power generation, material degradation due to hydrogen embrittlement* and ammonia corrosion occurs at various locations, including storage facilities and combustion equipment. To analyze and evaluate the effects of hydrogen embrittlement and ammonia corrosion on various materials, it is important to select the most appropriate analytical methods and analytical equipment.
*Hydrogen embrittlement: sudden fracture of steel under stress after a certain period of time due to hydrogen ingress, such as corrosion from the service environment or exposure to hydrogen gas.
HORIBA Solutions >>
For analyzing and evaluationg hydrogen in metals: Glow Discharge Optical Emission Spectrometer GD-Profiler 2
For analyzing metal surfaces: Foreign Material Analysis by Raman Analysis
HORIBA combines the know-how of internal combustion engine exhaust gas measurement that has been cultivated over many years in response to customer requests and the newly acquired know-how of hydrogen and fuel cell evaluation to offer a wide range of solutions, from the construction or modification of engine test chambers for the development of hydrogen engines, to the provision of hydrogen meters and nitrogen compound analyzers, as well as analyzers in metals necessary for the prevention of hydrogen embrittlement.
For more information, please contact us.
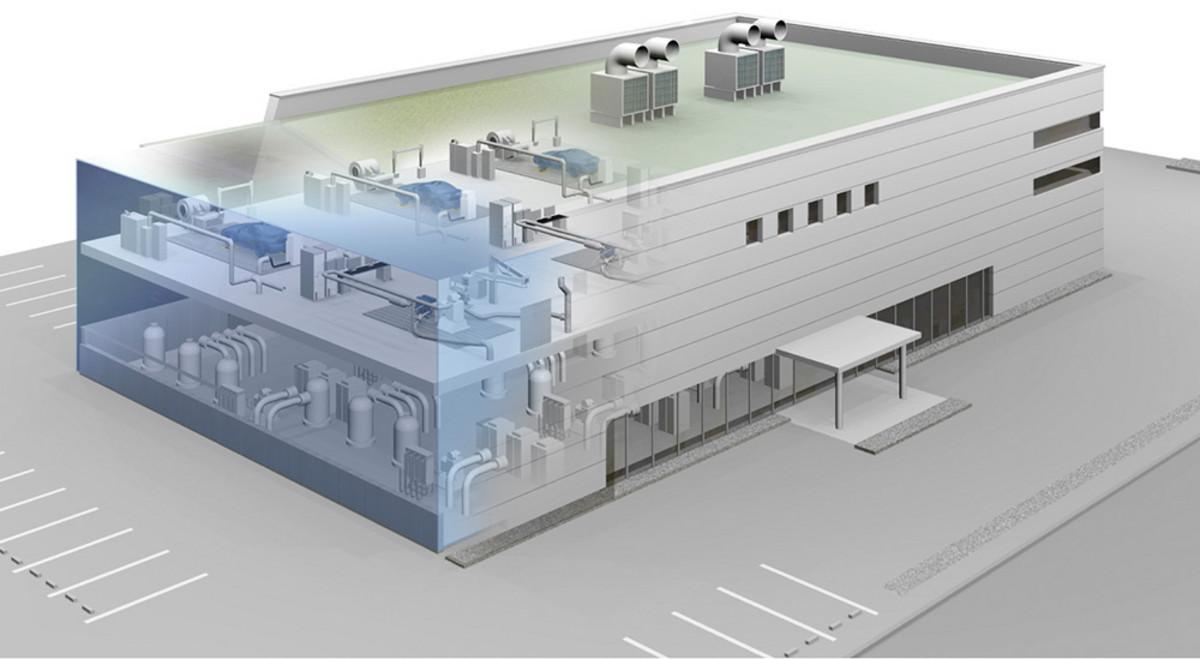
When launching a test building to handle hydrogen, more stringent safety measures are required than before.
Our turnkey solution, a total laboratory construction package, includes ordering multiple contractors, meetings to determine specifications, safety, process and quality control of construction, as well as post-introduction operation, maintenance, and work efficiency, all with an emphasis on safety and ease of use until just before the start of laboratory operations. We can handle the entire construction process on behalf of our busy customers.
HORIBA's Hydrogen Solutions
HORIBA STARS Enterprise Automotive Facility Management
Application Laboratory Virtual Tour
Do you have any questions or requests? Use this form to contact our specialists.